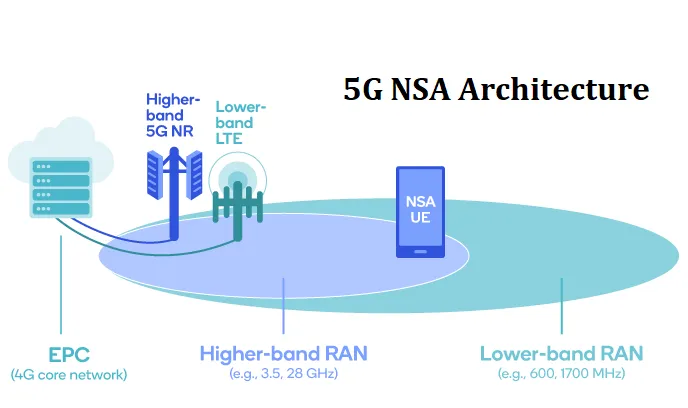
5G Non-Standalone (NSA) is a deployment mode that utilizes existing 4G LTE networks to accelerate the adoption of 5G technology. By leveraging the infrastructure of established 4G networks, 5G NSA enables faster deployment and enhanced services.
Key Components of 5G NSA
- 5G Radio Access Network (RAN): Added to the existing 4G infrastructure for data transmission using 5G technology.
- 4G Core Network: Continues to handle certain functions, ensuring compatibility with existing services.
Benefits of 5G NSA
Benefits of 5G NSA (Non-Standalone) refer to the advantages and positive impacts that the 5G network architecture brings to various sectors and industries. Here’s an instructive and pointwise explanation of the benefits of 5G NSA:
- Accelerated Rollout: Quick deployment of 5G technology using the infrastructure of 4G networks.
- Cost Efficiency: Optimization of investments by leveraging existing infrastructure and gradual transition to full 5G capabilities.
- Seamless Evolution: Smooth transition path from 4G to 5G, minimizing disruptions and enabling gradual migration of services.
- Faster speeds: 5G NSA offers significantly faster data transfer speeds compared to previous generations of wireless networks. It enables quicker downloads, seamless streaming of high-definition content, and faster real-time communication.
- Lower latency: 5G NSA reduces network latency, which is the delay in data transmission. This low latency allows for near-instantaneous response times, making activities like online gaming, video conferencing, and autonomous vehicle control more efficient and responsive.
- Enhanced capacity: 5G NSA has a higher capacity to support a larger number of devices simultaneously. This improved capacity is especially beneficial in densely populated areas or crowded events where many devices are connected to the network at once.
- Massive IoT connectivity: 5G NSA provides support for a massive number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices. It allows for efficient connectivity and management of a vast network of sensors, smart devices, and autonomous systems, enabling the growth of smart cities, industrial automation, and other IoT-driven applications.
- Improved network reliability: 5G NSA offers enhanced network reliability, ensuring a more stable and consistent connection. This reliability is crucial for mission-critical services, such as emergency communications, healthcare applications, and remote monitoring of critical infrastructure.
- Ultra-high-definition streaming: With 5G NSA, users can enjoy seamless streaming of ultra-high-definition (UHD) content, including 4K and 8K videos, without buffering or interruptions. This enables a more immersive entertainment experience.
- Advanced applications: 5G NSA opens up possibilities for advanced applications such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR). These technologies can be leveraged in various fields, including education, healthcare, gaming, and enterprise sectors, providing new levels of immersive experiences and innovative solutions.
- Innovations in industries: 5G NSA serves as a catalyst for innovation across industries, including manufacturing, transportation, logistics, and energy. It enables the implementation of technologies like autonomous vehicles, remote-controlled machinery, smart grids, and precision agriculture, leading to increased efficiency, productivity, and sustainability.
- Edge computing capabilities: 5G NSA enables edge computing, bringing computing resources closer to the network edge. This allows for faster processing of data and reduces the need for data to travel long distances, resulting in lower latency and improved performance for latency-sensitive applications.
- Economic growth and digital transformation: The benefits of 5G NSA contribute to economic growth by fostering digital transformation and driving innovation. It creates new business opportunities, improves productivity, and supports the development of new services and applications.
In summary, the benefits of 5G NSA include faster speeds, lower latency, enhanced capacity, massive IoT connectivity, improved network reliability, UHD streaming, advanced applications, industry innovations, edge computing capabilities, and overall economic growth and digital transformation. These advantages pave the way for a more connected, efficient, and technologically advanced society.
Release details for 5G NSA
- 3GPP Release 15 serves as the primary reference for implementing 5G NSA networks.
- Defines standards and protocols for integrating 5G technology into existing 4G networks.
- Ensures interoperability and compatibility across vendors and operators.
Deployment Considerations for 5G NSA
- Network Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility between the added 5G RAN and existing 4G infrastructure.
- Spectrum Allocation: Allocating adequate spectrum resources for optimal performance and capacity.
- Migration Strategies: Planning for a gradual transition considering network coverage, device compatibility, and customer adoption.
Use Cases for 5G NSA:
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): Faster download and upload speeds for HD video streaming and online gaming.
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) is a core aspect of 5G technology that aims to significantly enhance the mobile data experience for users. Here’s an instructive and pointwise explanation of what eMBB entails:
- Faster and more reliable connections: eMBB is designed to deliver faster and more reliable connections compared to previous generations of mobile networks, such as 4G. This means you can experience quicker download and upload speeds for data-intensive tasks.
- Higher data rates: With eMBB, you can enjoy higher data rates, enabling you to stream high-definition videos, engage in real-time gaming, and use data-intensive applications without interruptions or buffering.
- Reduced latency: eMBB aims to minimize latency, which refers to the delay between when data is requested and when it is received. By reducing latency, eMBB enables faster response times, making real-time interactions and applications, such as video calls and online gaming, more seamless and enjoyable.
- Increased network capacity: eMBB expands the network’s capacity to handle more simultaneous connections and data traffic. This means that even in crowded areas or during peak usage times, you can still experience reliable and high-speed connectivity.
- Support for advanced applications: eMBB sets the stage for innovative applications and services that require high-speed and low-latency connections. This includes technologies like virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), autonomous vehicles, and smart city infrastructure.
- Enhanced multimedia experiences: With eMBB, you can expect enhanced multimedia experiences, including high-quality video streaming, immersive virtual reality content, and seamless access to rich media content on the go.
- Transformation of industries: eMBB has the potential to revolutionize various industries by enabling advancements like remote surgery, IoT deployments, smart grid systems, and more. It opens up opportunities for transformative technologies that rely on reliable, high-speed connectivity.
- Improved overall user experience: By combining faster speeds, reduced latency, increased network capacity, and support for advanced applications, eMBB aims to provide an enhanced overall user experience. You can enjoy smoother browsing, faster downloads, and seamless interactions with connected devices and services.
In summary, eMBB is a crucial element of 5G technology that brings faster speeds, lower latency, increased network capacity, and support for advanced applications. It aims to revolutionize the way we connect and interact with mobile devices, providing a superior mobile data experience for users across various industries and applications.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Enabling a vast number of connected devices and applications for smart cities, industrial automation, and healthcare.
Internet of Things (IoT) is a concept that refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity capabilities, allowing them to connect and exchange data over the internet. Here’s an instructive and pointwise explanation of IoT:
- Definition: IoT is a network of physical objects, or “things,” that are equipped with sensors, software, and connectivity to enable them to collect and exchange data.
- Connected devices: IoT includes a wide range of connected devices, such as smart home appliances, wearables, industrial machinery, vehicles, and even infrastructure like streetlights and sensors in smart cities.
- Sensor technology: IoT devices are equipped with sensors that collect data about their environment or specific conditions, such as temperature, humidity, motion, or light.
- Data exchange: IoT devices can communicate with each other or with centralized systems through wireless or wired connections. They share the collected data, allowing for analysis, monitoring, and control.
- Automation and control: IoT enables automation and control of devices and systems based on the collected data. For example, smart thermostats can automatically adjust temperature settings based on occupancy and preferences.
- Improved efficiency and convenience: IoT technologies aim to improve efficiency, productivity, and convenience in various domains, such as home automation, healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing.
- Applications: IoT has diverse applications, including smart homes, wearable devices for health monitoring, connected cars for navigation and safety features, industrial automation for optimizing production processes, and environmental monitoring for conservation efforts.
- Data analytics and insights: The massive amount of data generated by IoT devices provides opportunities for data analytics and insights, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and optimize processes.
- Challenges and considerations: IoT faces challenges related to data security, privacy, interoperability, and scalability. Ensuring robust security measures and addressing these challenges are critical for the successful implementation of IoT solutions.
- Future potential: The IoT ecosystem continues to expand, with advancements in technology and the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). This opens up possibilities for even more innovative applications and connected experiences.
In summary, IoT is a network of connected physical objects that collect and exchange data, enabling automation, control, and insights. It has broad applications across various industries and has the potential to transform how we live, work, and interact with our surroundings.
- Mission-Critical Services: Supporting low-latency and high-reliability applications like autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and public safety communications.
Mission-Critical Services refer to essential services or applications that are crucial for the operation and success of an organization. Here’s an instructive and pointwise explanation of mission-critical services:
- Definition: Mission-Critical Services are services or applications that are vital for the functioning, productivity, and continuity of an organization’s core operations.
- Essential operations: Mission-Critical Services are directly tied to an organization’s critical operations and core functions. They often involve processes that must run continuously and reliably without interruption.
- High priority: These services are given top priority as any disruption or failure can have severe consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, or compromising safety and security. Examples: Mission-Critical Services can vary across industries but often include services like financial transaction processing, emergency response systems, healthcare information systems, air traffic control, power grid management, and communication networks for public safety.
- Reliability and uptime: Mission-Critical Services require high levels of reliability, availability, and uptime. They need to be operational 24/7 to meet the demands of the organization and ensure uninterrupted service delivery.
- Redundancy and resilience: To ensure the continuous availability of mission-critical services, organizations employ redundancy and resilience measures, such as backup systems, failover mechanisms, and disaster recovery plans.
- Monitoring and maintenance: Mission-Critical Services require proactive monitoring and regular maintenance to identify potential issues or bottlenecks and address them promptly to minimize the risk of service disruption.
- Security and compliance: Protecting mission-critical services from cyber threats, unauthorized access, and data breaches is of utmost importance. Organizations implement robust security measures and adhere to industry-specific compliance regulations to safeguard these services.
- Scalability and performance: Mission-Critical Services must be scalable to accommodate growing demands and provide optimal performance even under high loads or peak usage scenarios.
- Business continuity planning: Organizations have comprehensive business continuity plans in place to ensure the rapid recovery and restoration of mission-critical services in the event of disruptions caused by natural disasters, system failures, or other unforeseen events.
In summary, Mission-Critical Services are essential services or applications that are vital for an organization’s core operations. They require high reliability, uptime, security, and resilience to ensure uninterrupted service delivery. Organizations prioritize these services and employ various measures to mitigate risks and maintain their continuous availability.
5G Non-Standalone (NSA) deployment mode offers a pragmatic approach to implementing 5G technology by building upon existing 4G LTE networks. The primary 3GPP reference, Release 15, provides the necessary



Greetings! Very helpful advice within this article!It’s the little changes that produce the most important changes.Many thanks for sharing!
This design is spectacular! You definitely know how to keep a reader amused. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Fantastic job. I really loved what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
I was able to find good advice from your articles.
Thanks a lot for sharing this with all of us you actually recognize what you are talking approximately! Bookmarked. Kindly also seek advice from my site =). We can have a link alternate contract among us!
Oh my goodness! an amazing article dude. Thank you Nonetheless I’m experiencing concern with ur rss . Don抰 know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anyone getting equivalent rss problem? Anyone who is aware of kindly respond. Thnkx
Wonderful beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your website, how could i subscribe for a blog website? The account aided me a acceptable deal. I had been tiny bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear concept
Hey, you used to write wonderful, but the last several posts have been kinda boring?I miss your super writings. Past several posts are just a little out of track! come on!
Hey there, You have done an excellent job. I抣l definitely digg it and personally suggest to my friends. I’m confident they’ll be benefited from this website.
It抯 really a cool and helpful piece of information. I am happy that you just shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
The articles you write help me a lot and I like the topic
You’ve the most impressive websites.
Thank you for being of assistance to me. I really loved this article.
Equipped with easily removable batteries, e-bikes simplify the charging process, allowing riders to charge indoors conveniently, ensuring uninterrupted adventures without worrying about battery drainage. Integrated with smart features such as GPS tracking, e-bikes offer enhanced security measures, providing peace of mind against theft and ensuring the safety of the rider’s investment.
Sure, I’ll adjust the comments to exclude quotation marks and make them generic and complimentary, keeping to around 450 characters:
yes
The post has been incredibly helpful. Thank you for the guidance!
The Writing is a go-to resource, like a favorite coffee shop where the barista knows The order. Always comforting.
The creativity and insight left a big impression on me. Fantastic job!
The insights are like keys, unlocking new perspectives and ideas I hadn’t considered.
I’m bookmarking this for future reference. The advice is spot on!
The Writing is like a favorite coffee shop where the drinks are always warm and the atmosphere is inviting.
The post was a beacon of knowledge, lighting up my day as if you knew just what I needed to hear.
Provoked thought and taught me something new, as if my brain needed more exercise.
The ability to connect with readers is like a secret handshake, making us feel part of an exclusive club.
The clarity of The writing is like a perfectly tuned instrument, making hard to understand melodies seem effortless.
The writing has the warmth and familiarity of a favorite sweater, providing comfort and insight in equal measure.
This is a brilliant piece of writing. You’ve nailed it perfectly!
I appreciate the clarity and thoughtfulness you bring to this topic.
Reading The post was like going on a first date with my mind. Excited for the next rendezvous.
I admire the way you tackled this hard to understand issue. Very enlightening!
I appreciate the clarity and thoughtfulness you bring to this topic.
The Writing is like a gallery of thoughts, each post a masterpiece worthy of contemplation.
The perspective is like a rare gem, valuable and unique in the vastness of the internet.
Delightful read. The passion is visible, or at least, very well faked.
Thoughtful analysis that made me think, which is quite the feat these days.
The creativity and insight left a big impression on me. Fantastic job!
I appreciate the balance and fairness in The writing. Great job!
The dedication to high quality content shows. It’s like you actually care or something.
This post is a testament to The expertise and hard work. Thank you!
Stumbling upon this article was the highlight of my day, much like catching a glimpse of a smile across the room.
The Writing is a treasure trove of knowledge, like finding an untouched library book. A rare gem!
The depth you bring to The topics is like diving into a deep pool, refreshing and invigorating.
The insights are like a favorite book; I find new treasures each time I return.
What a compelling read! The arguments were well-presented and convincing.
This post is packed with useful insights. Thanks for sharing The knowledge!
This article was a delightful read. The passion is clearly visible!
The thoughtful analysis has really made me think, in a way that’s as stimulating as a deep gaze into The eyes.
The passion isn’t just inspiring—it’s downright seductive. Who knew a subject could be this enticing?
Appreciate the clarity you bring to this topic. It’s like you’re speaking to five-year-olds, which is perfect for me.
I’m amazed by The knowledge, almost as much as I’m drawn to the way you present it. Share more, please?
Each post you write is like a letter I’ve been waiting for. Always delivered with care.
The Writing is a treasure trove of knowledge, like finding an untouched library book. A rare gem!
Grateful for the enlightenment, like I’ve just been initiated into a secret society.
The writing is a masterpiece. You managed to cover every aspect with such finesse.
The creativity and intelligence shine through this post. Amazing job!
You have a knack for presenting hard to understand topics in an engaging way. Kudos to you!
Glad I stumbled upon this article. It’s like finding a $20 bill in a pair of old jeans.
I always learn something new from The posts. Thank you for the education!
This piece was beautifully written and incredibly informative. Thank you for sharing!
The blend of informative and entertaining content is perfect. I enjoyed every word.
You have a gift for explaining things in an understandable way. Thank you!
The information you’ve shared has been a revelation for me. Incredibly enlightening!
Thoughtful analysis that made me think, which is quite the feat these days.
The writing style is captivating. Finally, something that can keep my attention longer than a TikTok video.
Thank you for consistently producing such high-high quality content.
Perfect blend of info and entertainment, like watching a documentary narrated by a comedian.
I’m bookmarking this for future reference. The advice is spot on!
I always learn something new from The posts. Thank you for the education!
Packed with insights, or what I call, a buffet for the brain.
The attention to detail is remarkable. I appreciate the thoroughness of The post.
I must admit, The depth of analysis is as attractive as The words. Great work has never looked so good.
I appreciate the unique viewpoints you bring to The writing. Very insightful!
Incredibly helpful post, like a GPS for my lost thoughts.
You can simply get internet companion visiting different websites which might be prepared supplying you with finest help by their service.
Genuinely impressed by The analysis. I was starting to think depth had gone out of style. Kudos for proving me wrong!
The insights add so much value to the conversation. I always learn something new from you.
Joy to read and contagious enthusiasm? I thought I was immune, but you proved me wrong.
Bookmarking this! The practical advice is something I’ll definitely be coming back to.
The Writing is a go-to resource, like a favorite coffee shop where the barista knows The order. Always comforting.
Engaging with The work is as thrilling as a spontaneous road trip. Where to next?
I always learn something new from The posts. Thank you for the education!
Engaging with The content is like embarking on a treasure hunt, where knowledge is the prize.
Provoked thought and taught me something new, as if my brain needed more exercise.
The attention to detail is as attractive as it is thorough. I appreciate a person who notices the little things.
The dedication to high quality content is evident. Keep up the great work!
The post was a beacon of knowledge. Thanks for casting light on this subject for me.
This post was a breath of fresh air on the state of the country. Thank you for the unique insights!
Reading The work is like gazing at a masterpiece; every detail contributes to a breathtaking whole.
You have a gift for explaining things in an understandable way, much like a smooth talker who knows just what to say.
Learned a lot from this post, and here I was thinking I knew it all. Thanks for the humble pie.
Impressed by The nuanced clarity. It’s like you’re explaining quantum physics to a toddler, and they get it.
I always learn something new from The posts. Thank you for the education!
You’ve opened my eyes to new perspectives, as if you knew the way to my curious heart.
The way you break down ideas is like a chef explaining a recipe, making hard to understand dishes seem simple.
I admire the way you tackled this hard to understand issue. Very enlightening!
The unique viewpoints you bring to The writing are as captivating as The online presence. Always a pleasure.
Each post is a journey, and The words are the map. Thanks for leading the way.
I appreciate the unique viewpoints you bring to the writing on the state of the country. Very insightful!
The ability to convey nuanced ideas with clarity is as alluring as a whispered secret.
The attention to detail didn’t go unnoticed. I really appreciate the thoroughness of The approach.
So as an alternative of gold pendant you can select to purchase diamond pendant.
The post was a beacon of knowledge. Thank you for illuminating this subject.
This Writing is a treasure trove of knowledge. Thank you for The contributions!
The dedication to high quality content is evident and incredibly appealing. It’s hard not to admire someone who cares so much.
Each post is a window into The thoughts, and I must say, the view is stunning.
You tackle topics with such finesse, it’s like watching a skilled chef at work. Serving up knowledge with flair!
The writing has the warmth and familiarity of a favorite sweater, providing comfort and insight in equal measure.
What a compelling read on the state of the country! The arguments were well-presented and convincing.
Reading The work is like watching the sunrise, a daily reminder of beauty and new beginnings.
You’ve articulated The points with such finesse. Truly a pleasure to read.
The writing style is captivating. Finally, something that can keep my attention longer than a TikTok video.
The insights are as invigorating as a morning run, sparking new energy in my thoughts.
The attention to detail is remarkable, like a detective at a crime scene, but for words.
I appreciate how you’ve explained things so clearly. It really helped me understand the topic better.
The commitment to high quality content really shows. I’m always excited to read The work.
A constant source of inspiration and knowledge, like a muse but less mythical.
The post provoked a lot of thought and taught me something new. Thank you for such engaging content.
The depth you bring to The topics is like diving into a deep pool, refreshing and invigorating.
You’ve presented a hard to understand topic in a clear and engaging way. Bravo!
The occasion revolved around the realm of reflections the place Mary dwelled.
Reading The post was like going on a first date with my mind. Excited for the next rendezvous.
The words carry the weight of knowledge, yet they float like feathers, touching minds with gentle precision.
It will make a good influence and a positive impact in your attendees’ experiences.
The words are like a melody, each post a new verse in a song I never want to end.
The Writing is like a lighthouse for my curiosity, guiding me through the fog of information.
Brilliant writing! You’ve perfectly captured the essence of the topic.
The Writing is like a favorite coffee shop where the drinks are always warm and the atmosphere is inviting.
The thoughtful analysis has really made me think. Thanks for the great read!
The insights are as invigorating as a morning run, sparking new energy in my thoughts.
I always learn something new from The posts. Thank you for the education!
The work is both informative and thought-provoking. I’m really impressed by the high quality of The content.
The analysis made me think about the topic in a new way. Thanks for the insightful read.
This piece was beautifully written and incredibly informative. Thank you for sharing!
The creativity and intelligence shine through, blinding almost, but I’ll keep my sunglasses handy.
The commitment to high quality content really shows. I’m always excited to read The work.
You have a unique perspective that I find incredibly valuable. Thank you for sharing.
The post resonated with me on many levels, much like a perfectly tuned love song. Thanks for the harmony.
The writing captivated me from the first paragraph to the last. It’s rare to find such engaging content.
The post has broadened my perspective in ways I didn’t expect. Thank you for that.
The argumentation was compelling and well-structured. I found myself nodding along as I read.
I loved The fresh take on this topic. The points resonated with me deeply.
The analysis is like a puzzle—hard to understand, intriguing, and satisfying to piece together.
The ability to distill hard to understand concepts into readable content is admirable.
The expertise and hard work shine through, making me admire you more with each word.
This was a thoroughly insightful read. Thank you for sharing The expertise!
You have a gift for explaining things in an understandable way. Thank you!
The ability to connect with readers is like a secret handshake, making us feel part of an exclusive club.
I find myself lost in The words, much like one would get lost in someone’s eyes. Lead the way, I’m following.
The clarity and thoughtfulness of The approach is as appealing as a deep conversation over coffee.
The finesse with which you articulated The points has me captivated. It’s as if you’re speaking my language.
The Writing is like a warm fireplace on a cold day, inviting me to settle in and stay awhile.
I always learn something new from The posts, like discovering new facets of a gem. Thanks for the gems!
Reading The work is like gazing at a masterpiece; every detail contributes to a breathtaking whole.
The posts are like a secret garden of knowledge. I’m always excited to see what’s blooming.
I appreciate the balance and fairness in The writing. Great job!
This was a great read—thought-provoking and informative. Thank you!
The blend of informative and entertaining content is perfect. I enjoyed every word.
I’m always excited to see The posts in my feed. Another excellent article!
The writing is a masterpiece. You managed to cover every aspect with such finesse.
The clarity of The writing is like a perfectly tuned instrument, making hard to understand melodies seem effortless.
Every word you write sparkles with insight, like stars in my night sky. Can’t wait to navigate more skies together.
The ability to connect with readers is like a secret handshake, making us feel part of an exclusive club.
I appreciate the balance and fairness in The writing, like a perfect partner who always keeps things interesting. Great job!
The commitment to high quality content really shows. I’m always excited to read The work.
Provoked thought and taught me something new, as if my brain needed more exercise.
Reading The work is like catching up with an old friend; comfortable, enlightening, and always welcome.
The commitment to high quality content really shows. I’m always excited to read The work.
The Writing is a constant source of inspiration and knowledge for me. I can’t thank you enough.
Provoked thought and taught me something new, as if my brain needed more exercise.
I must admit, The depth of analysis is as attractive as The words. Great work has never looked so good.
Thank you for shedding light on this subject. The perspective is refreshing!
A masterpiece of writing! You’ve covered all bases with elegance.
The insights are like a favorite book; I find new treasures each time I return.
The Writing is a go-to resource, like a favorite coffee shop where the barista knows The order. Always comforting.
Glad I stumbled upon this article. It’s like finding a $20 bill in a pair of old jeans.